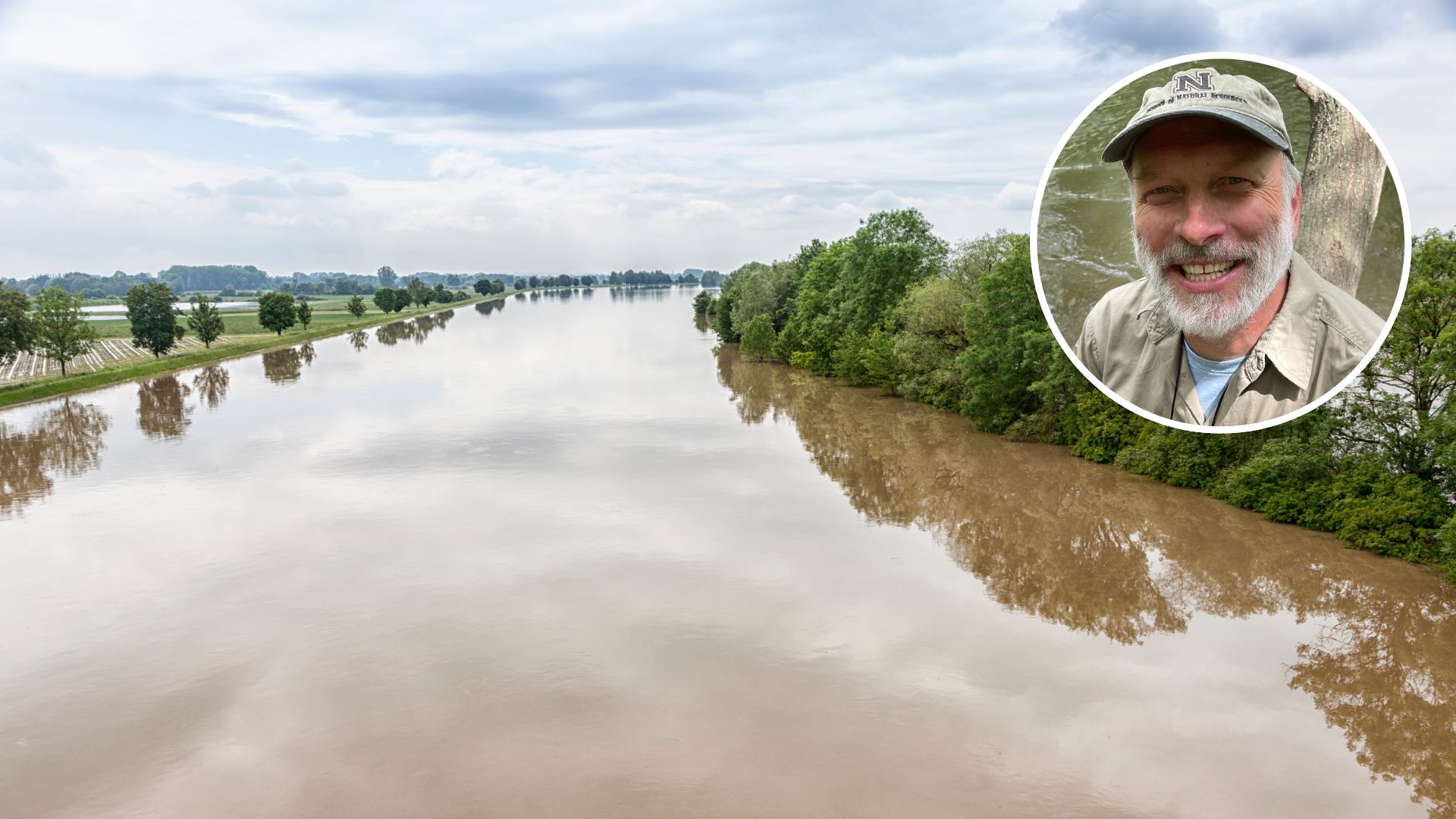
Australians have seen their share of flood waters over the past few years but do you know who isn’t sick of floods yet? Plants and animals are living their best lives, according to a study involving a Charles Sturt University biology expert.
By Charles Sturt Associate Professor in Biology with the School of Agricultural, Environmental and Veterinary Sciences Paul Humphries (pictured, inset) and Lecturer at Charles Darwin University Keller Kopf.
Humans, as a rule, do not like floods. And three years of La Niña rains have meant Australians have had more than enough of floods.
But Australia’s plants and animals have evolved alongside periodic floods, as they have for fire. For them, floods are a boon. These pulses of water are vital to the health of most river floodplain ecosystems. For some native fish, floods create new habitat as the waters fill floodplains, wetlands and creeks. Many trees like river red gums need periodic flooding too.
Floods trigger a huge spike in growth. Nutrient-rich sediment is washed downstream and out on to floodplains. This is a boon to algae and aquatic plants at first, and, once the water evaporates, to grasses, shrubs and trees. Herbivores such as wallabies and wombats feast on the new growth.
Most of the time, rivers stay in their main channels and floodplains are dry. But in years like this one, so much rain falls that water spills over the banks and fills floodplains. This is a life-giving process which nourishes and replenishes. Without floods, rivers would not be rivers – they’d just be drains, unfit for all but the very hardiest of animals and plants.
Why does nature need floods?
It’s not all good news for nature. Flooding is a disturbance for wildlife and plants, moving things around and shaking things up. Some animals may drown, high flows may rip out plants and even undermine and topple trees. Low-oxygen blackwater events and fish kills – heartbreaking for many – often follow floods, as they have recently on the Murray. But after the damage comes the boom.
Once the initial pulse of water subsides, it often takes much longer for the water to evaporate or drain from the floodplains. Plants killed by the water will add to the organic matter load, which may later be used by other plants.
The pulse of nutrients that goes with flooding is wonderful for freshwater phytoplankton (miniscule aquatic plants), as well as zooplankton which feed on them, such as tiny rotifers, known as wheel animals, and crustaceans. Some fish leave the main channel of the river and swim onto their new temporary habitat, feeding on the zooplankton. Waterbirds follow them.
Should the timing be right, native fish like golden and silver perch may breed in floodplain wetlands. Their larvae are poor swimmers, and these still, food-rich water bodies are ideal nurseries.
South Australia’s Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre has only filled a handful of times over the last century. But the unprecedented rains this year have partly filled the lake. When water covers the arid land, brine shrimp eggs hatch in their millions and start feeding and breeding. It’s a brief boom for fish, but as the water evaporates, the lake gets saltier and eventually kills the fish. Pelicans, cormorants, terns and gulls head inland to feast on shrimp and dying or dead fish.
In northern Australia, many rivers are not dammed, and widespread natural flooding occurs most years. Indigenous people here are accustomed to living alongside flooding and have been making use of the riches of floodplain productivity for more than 50,000 years. Tropical floodplains offer food and habitat to everything from aquatic plants and barramundi to saltwater crocodiles and magpie geese.
In Australia’s south-east, floodwaters generally don’t linger quite as long as they do in the tropical north. But they do rise rapidly – sometimes several metres over only a couple of days. Much of the water will never return to the main channel of the river but will evaporate slowly. Deeper remnants like billabongs, lagoons or oxbow lakes – actually old river channels – linger longest.
The giant of Australia’s rivers, the Murray, takes longer to flood because Australia is mostly flat. Pulses of water move slowly down its tributaries to the main channel. It can take weeks to months for rain that falls on the Great Dividing Range to make it to the Murray’s mouth at Goolwa in South Australia.
These lingering floodwaters are perfect for freshwater mussels, as well as frogs, lizards, platypus and snakes. Bottlebrushes, wattles, reeds, rushes and aquatic plants do well out of floods too.
Of course, introduced species often thrive too. Common carp populations typically boom after floods. And willow trees and other invasive aquatic plants that spread through pieces breaking off, do well on the back of floods.
Our uneasy relationship with rivers
Nature needs floods. But while you might not believe it, we need them too. Most of the world’s major cities were founded next to rivers, which gave their inhabitants water, fish, transport, and fertile farmland. But for all river cities, there are times when the river surges and can destroy houses and livelihoods.
Many cities have tried to tame floods with levees and dams. But as we’re finding now, you can reduce the impact of smaller floods – but the big ones are all but unstoppable.
Because we have farmed and settled so many floodplains, farmers are particularly vulnerable to floods. Floodwaters hitting bush will be slowed by trees and plants. But farms are often cleared, which can see more erosion take place. Whole farms can be devastated by flooding, leading to food prices spiking.
With climate change, Australia is expected to experience bigger and more frequent floods. This may be a good thing for nature but means people will no longer be able to live safely in some places. It will also mean iconic ecosystems like Kakadu will be at risk, with sea level rise predicted to push saltwater into almost half of its famous wetlands by 2070.
While floods bring pain in the short term, over the longer term both humans and nature need the benefits they bring.
This article first appeared on The Conversation.





Social
Explore the world of social